FMF Certification
Nuchal translucency scan
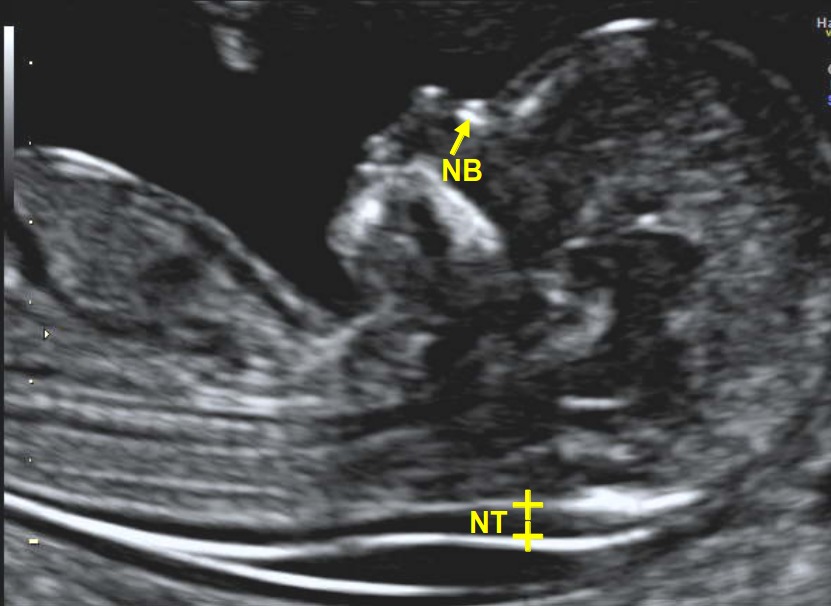
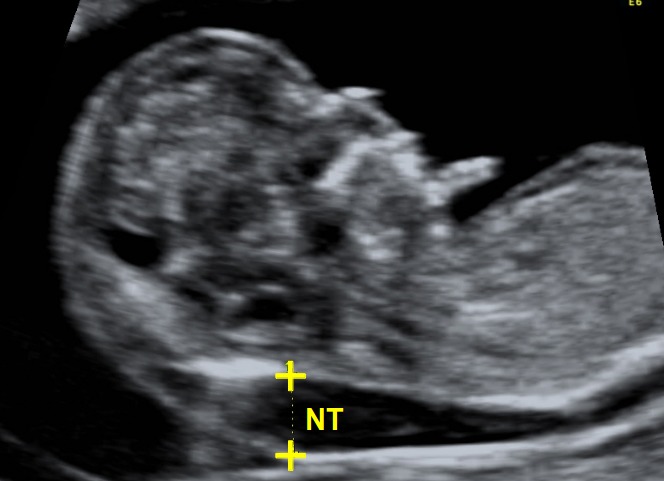
Nuchal translucency (NT) is the sonographic appearance of a collection of fluid under the skin behind the fetal neck in the first-trimester of pregnancy. The term translucency is used, irrespective of whether it is septated or not and whether it is confined to the neck or envelopes the whole fetus. In fetuses with chromosomal abnormalities, cardiac defects and many genetic syndromes the NT thickness is increased.
Screening by NT can detect about 80% of fetuses with trisomy 21 and other major aneuploides for a false positive rate of 5%. The combination of NT and maternal serum free β-hCG and PAPP-A improves the detection to 90%. There is now evidence that the detection rate can increase to about 95% and the false positive rate can be reduced to 3% by also examining the nasal bone, ductus venosus flow and tricuspid flow.
Early screening for chromosomal abnormalities
The Fetal Medicine Foundation (FMF) has introduced a process of comprehensive training, support and audit for the proper implementation of early screening for chromosomal abnormalities. The FMF advocates that effective screening requires:
- Carrying out the ultrasound examination by appropriately trained sonographers.
- Measurement of maternal serum free β-hCG and PAPP-A by laboratories that can demonstrate good quality assurance performance.
- A risk calculation program that uses an algorithm based on scientific evidence. The software companies that use this algorithm are Astraia Software GmbH, ViewPoint GE Healthcare and Zeitgeist Health SE.
- Appropriate counselling of the parents.
Sonographers who have obtained the FMF Certificate in the nuchal translucency (NT) scan can obtain free of charge the FMF software for first-trimester screening for chromosomal abnormalities by maternal age, fetal NT thickness and maternal serum free β-hCG and PAPP-A. Should they wish to use the additional markers for chromosomal abnormalities (nasal bone, tricuspid flow and ductus venosus flow) they would need to obtain the appropriate FMF Certificate for each of these markers.
Normal nuchal translucency
High nuchal translucency
Requirements for certification
Please attend all online courses through our new FMF website.
From March 2026, registration will be required to qualify for a license extension for the risk calculation software. All new licenses will be issued exclusively through the new website.
To apply for a new license or request a license extension, please follow instructions published on your original FMF Page. Please continue using your original FMF page on this website to apply for and access compatible license files via the Software section.
Note: Some countries have additional certification requirements.
USA: Visit www.fetalmedicineusa.com for accreditation instructions and contact details.
Australia: Contact RANZCOG for accreditation and image submission details.
Further updates and requirements will be posted online soon.
Protocol for measurement
- The gestational period must be 11 to 13 weeks and six days.
- The fetal crown-rump length should be between 45 and 84mm.
- The magnification of the image should be such that the fetal head and thorax occupy the whole screen.
- A mid-sagittal view of the face should be obtained. This is defined by the presence of the echogenic tip of the nose and rectangular shape of the palate anteriorly, the translucent diencephalon in the centre and the nuchal membrane posteriorly. Minor deviations from the exact midline plane would cause non-visualization of the tip of the nose and visibility of the maxilla.
- The fetus should be in a neutral position, with the head in line with the spine. When the fetal neck is hyperextended the measurement can be falsely increased and when the neck is flexed, the measurement can be falsely decreased.
- Care must be taken to distinguish between fetal skin and amnion.
- The widest part of translucency must always be measured.
- Measurements should be taken with the inner border of the horizontal line of the callipers placed ON the line that defines the nuchal translucency thickness - the crossbar of the calliper should be such that it is hardly visible as it merges with the white line of the border, not in the nuchal fluid.
- In magnifying the image (pre or post freeze zoom) it is important to turn the gain down. This avoids the mistake of placing the calliper on the fuzzy edge of the line which causes an underestimate of the nuchal measurement.
- During the scan more than one measurement must be taken and the maximum one that meets all the above criteria should be recorded in the database.
- The umbilical cord may be round the fetal neck in about 5% of cases and this finding may produce a falsely increased NT. In such cases, the measurements of NT above and below the cord are different and, in the calculation of risk, it is more appropriate to use the average of the two measurements
