Fetal abnormalities » Multiple pregnancies
MC twins: twin anemia-polycythemia sequence
Prevalence:
- Spontaneous: 5% of monochorionic twins. Usually occurs >26 weeks' gestation.
- After laser ablation of placental vessels: 2-10% of monochorionic twins.
Ultrasound diagnosis:
- TAPS occurs due to a slow transfusion of blood from the donor to the recipient through few very small arteriovenous vascular anastomoses leading to highly discordant hemoglobin levels.
- There is no substantial difference between the twins in either size or amniotic fluid volume.
- The placenta of the anemic fetus looks thick and hyperechogenic, whereas that of the polycythemic fetus looks thin and translucent.
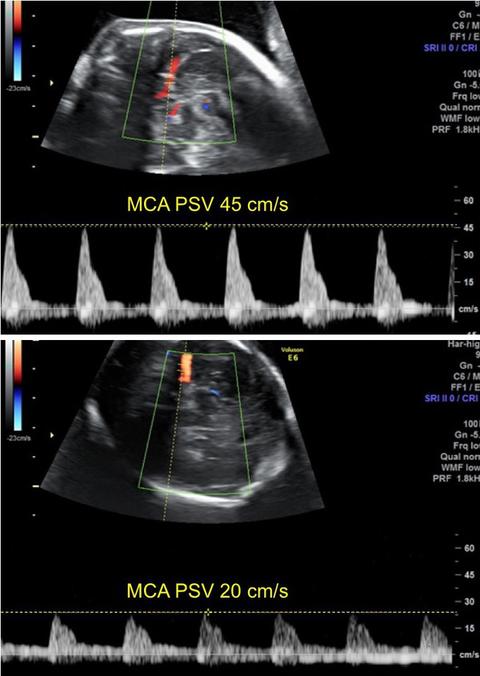
- The fetal middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity (MCA PSV) in the anemic fetus is increased (>1.5 multiples of median), whereas that in the polycythemic fetus is decreased (<1 multiples of the normal median).
- The anemic fetus may have a dilated heart, tricuspid regurgitation and ascites. The liver of the polycythemic fetus has a starry sky pattern due to diminished echogenicity of the liver parenchyma and an increased brightness of the portal venule walls.
Associated abnormalities:
- The incidence of chromosomal abnormalities, genetic syndromes or fetal defects is not increased.
Investigations:
- Detailed ultrasound examination, including echocardiography (to assess cardiac function) and measurement of MCA PSV (to predict degree of anemia and polycytemia).
Management:
- <26 weeks: endoscopic laser ablation of communicating placental vessels. Subsequently, scans every 1 week to monitor fetal growth, brain anatomy and MCA-PSV. Fetal brain MRI at ≥32 weeks’ gestation should be considered for the diagnosis of neuronal migration disorders. If both babies are developing normally vaginal delivery can be carried out at 37 weeks.
- 26-30 weeks: intrauterine blood transfusions to the anemic twin and exchange transfusion with Hartmans’ solution for the polycythemic twin. Doppler assessment every 2-3 days because it may become necessary to undertake interventions every 3-4 days. Delivery by cesarean section at 30-32 weeks.
- >30 weeks: delivery by cesarean section.
Prognosis:
- Neurodevelopmental delay in up to 20% of cases, which mainly depends on gestational age at birth. The risk is higher for the recipient twin.
Recurrence:
- No increased risk of recurrence.